
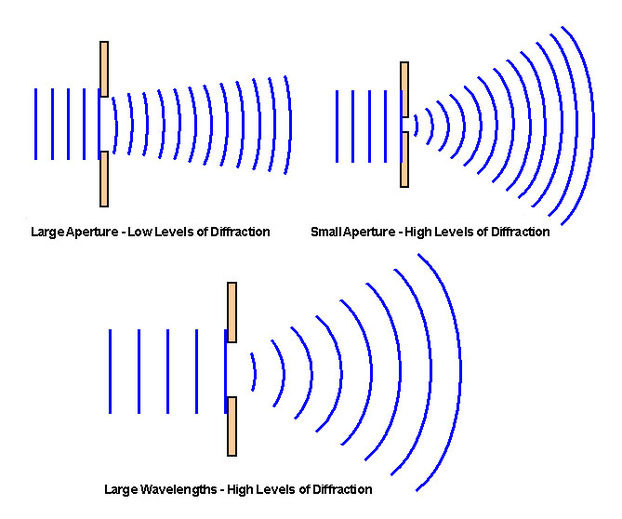
When the aperture is much larger than the wavelength, no diffraction occurs and when the aperture is smaller than wavelength, circular wavefronts are produced. The condition to obtain diffraction is that the dimensions of aperture or of the obstacle must be comparable to wavelength. What is Diffraction?īy definition, diffraction is the process by which a wave is spread out as a result of passing through a narrow aperture or across an edge, typically accompanied by interference between the waveforms produced. Also, the information provided in this tutorial will form the base for the next section. Therefore, please read it before jumping to other tutorials as this tutorial sheds light to many questions which will arise during the study of waves. What occurs to the shape of waves when they pass through a narrow gap? Do waves have the same shape as before?Īll these questions will get answer in this tutorial.
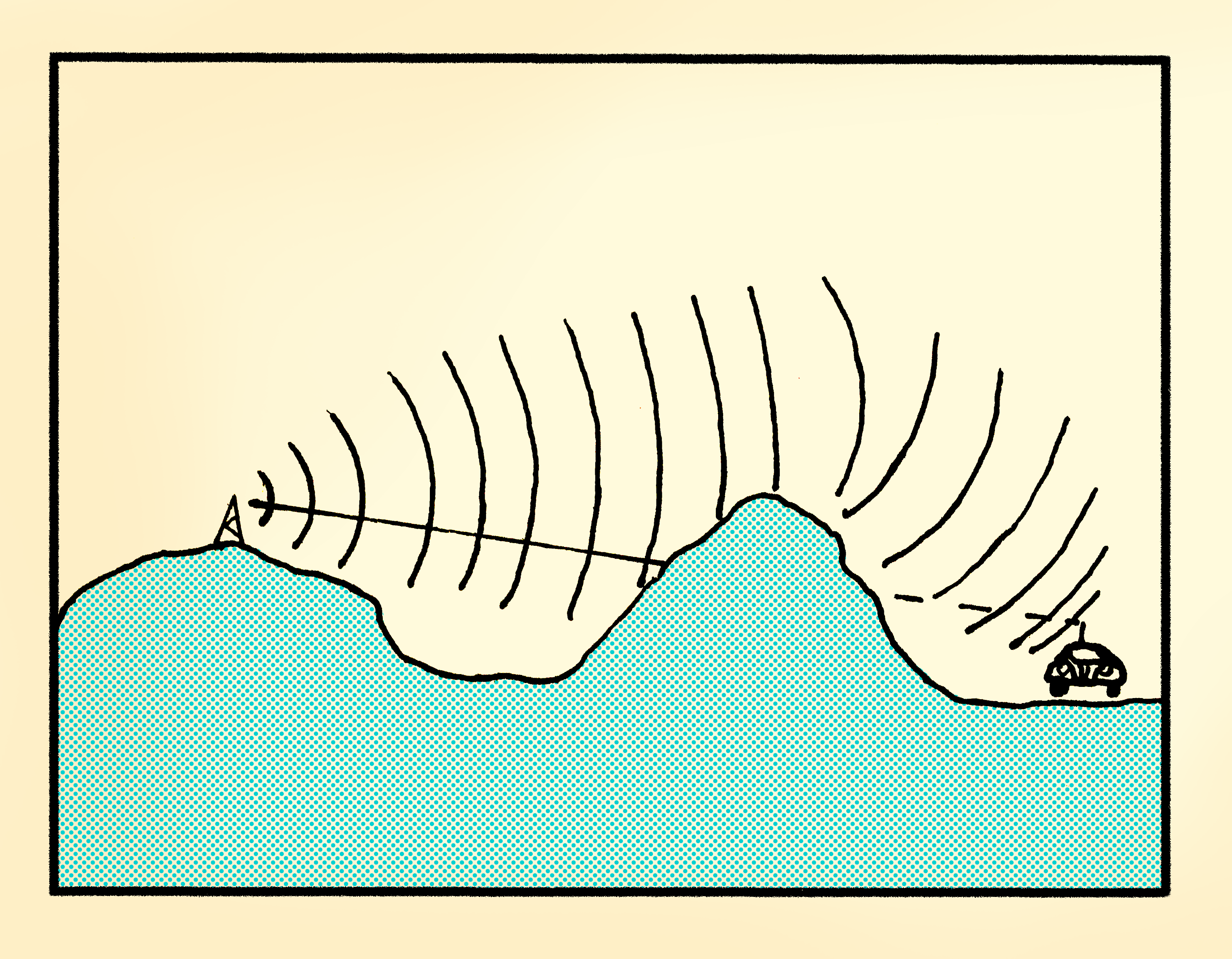
What happens to water waves when they encounter a stone during their path? Do they turn back or they continue moving on their way? What happens to water when you put a finger under the tap? Does water turn back on the tap or it continues falling down? Is the direction of water the same as before putting the finger under the tap? Why?

What is the relationship between diffraction and interference?.What happens to the shape of waves in diffraction?.What are the conditions for diffraction to occur?.In this Physics tutorial, you will learn:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
